Site search:
-
What’s new?
Energy for London Tags
Brent Buildings Camden Carbon Emissions CHP Cities Climate Adaptation Community Heating Community Initiatives Croydon Data DECC Decentralised Energy Distribution ECO Energy Costs Energy Efficiency Enfield FIT Fuel Poverty Funding Green Deal Hackney Haringey Housing Islington Lambeth Library Local Authorities Mayor Newham Ofgem Olympics Photovoltaics Planning RE:FIT RE:NEW Renewable Energy Retrofit Southwark Tower Hamlets Transport Waltham Forest Waste WestminsterEnergy Archives:
- February 2021 (1)
- January 2021 (15)
- December 2020 (15)
- November 2020 (9)
- October 2020 (3)
- August 2020 (5)
- July 2020 (3)
- June 2020 (4)
- April 2020 (10)
- March 2020 (5)
- February 2020 (2)
- January 2020 (3)
- October 2019 (1)
- September 2019 (4)
- August 2019 (2)
- July 2019 (1)
- August 2018 (1)
- November 2016 (8)
- October 2016 (8)
- September 2016 (2)
- August 2016 (8)
- July 2016 (14)
- April 2016 (12)
- March 2016 (16)
- February 2016 (8)
- January 2016 (4)
- December 2015 (1)
- November 2015 (1)
- October 2015 (16)
- September 2015 (3)
- June 2015 (1)
- May 2015 (1)
- April 2015 (1)
- March 2015 (1)
- February 2015 (1)
- January 2015 (1)
- December 2014 (18)
- November 2014 (4)
- August 2014 (8)
- July 2014 (7)
- June 2014 (25)
- May 2014 (8)
- April 2014 (4)
- March 2014 (12)
- February 2014 (7)
- January 2014 (13)
- December 2013 (11)
- November 2013 (15)
- October 2013 (15)
- September 2013 (18)
- August 2013 (5)
- July 2013 (20)
- June 2013 (33)
- May 2013 (8)
- April 2013 (16)
- March 2013 (25)
- February 2013 (14)
- January 2013 (20)
- December 2012 (23)
- November 2012 (23)
- October 2012 (25)
- September 2012 (14)
- July 2012 (12)
- June 2012 (43)
- May 2012 (20)
- April 2012 (8)
- March 2012 (40)
- February 2012 (39)
- January 2012 (40)
- December 2011 (22)
- November 2011 (40)
- October 2011 (33)
- September 2011 (48)
- August 2011 (40)
- July 2011 (58)
- June 2011 (41)
- May 2011 (80)
- April 2011 (38)
- March 2011 (33)
- February 2011 (25)
- January 2011 (24)
- December 2010 (3)
- November 2010 (7)
- October 2010 (6)
- September 2010 (7)
- August 2010 (1)
- July 2010 (2)
- June 2010 (4)
- May 2010 (1)
- March 2010 (3)
- February 2010 (3)
- December 2009 (5)
- November 2009 (2)
- October 2009 (3)
- July 2009 (3)
- June 2009 (1)
- April 2009 (1)
- March 2009 (1)
- February 2009 (1)
- January 2009 (1)
- December 2008 (2)
- October 2008 (1)
- September 2008 (1)
- July 2008 (1)
- March 2008 (2)
- January 2008 (2)
- October 2007 (1)
- September 2007 (3)
- July 2007 (1)
- March 2007 (1)
- February 2007 (3)
- November 2006 (3)
- August 2006 (1)
- February 2006 (1)
- May 2005 (1)
- February 2004 (1)
Search Results for: DUKES
Overview of CHP data
July 2014: CHP schemes – depending on size and fuel type – can benefit from a variety of government support mechanisms. These mostly take the form of partial exemptions from the Climate Change Levy, the Carbon Reduction Commitment (CRC), Carbon Floor Price, EU Emissions Trading Scheme, and business rates. Interaction with these mechanisms can be pretty complex at times (an overview of these are provided in the following presentations from an industry workshop last December) but critical to attaining these benefits is for the CHP scheme to achieve a ‘Good Quality’ status under the government’s CHPQA programme.
The CHPQA Standard highlights that the QA system has been place since around April 2001 providing “a methodology for assessing the quality of CHP Schemes in terms of their energy efficiency and environmental performance. This methodology is based on Threshold Criteria, which must be met or exceeded in order for the whole of the Scheme to qualify as ‘Good Quality’.” The QA programme also requires an annual submission from each CHP plant wishing to be classed as ‘Good Quality’ – and details on how to comply with this QA standard are set out in some comprehensive guidance notes posted on DECC’s CHPQA microsite here.
The CHPQA admits that “achieving CHPQA Certification may at first glance appear daunting” but fortunately, for the majority of schemes going forward in London (ie smaller scale), can access a more streamlined QA process which is available for <2MWe CHP plant (see guidance note 13). Overall, CHP schemes can be seen to go through some of the most rigorous monitoring requirements of all sustainable energy measures to receive government support.
CHP schemes in London that have achieved the CHPQA standard – and which have given consent for their details to be released – are listed on DECC’s Public CHP database here (set ‘region’ criteria to London). Aggregate CHP statistics are published in DECC’s Digest of UK Energy Statistics and regional (including London) data in the September issue of DECC’s Energy Trends journal. Further data can also be accessed on Ofgem’s CCL CHP register here. Additional detail on CHP and district heating schemes can be found on the London Heat Map.
Latest CHP data for London paints confusing picture…
27 September 2012: DECC’s latest issue of Energy Trends follows up from national Combined Heat and Power (CHP) dataset, published in July’s Digest of UK Energy Statistics (Chapter 7) (see also CHPA’s press release for further information on this), to present the data in a regional format, providing some detail on the use of CHP in London. The article – Combined Heat and Power in Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland and the regions of England in 2011 – can be downloaded here.
A number of things can be observed.
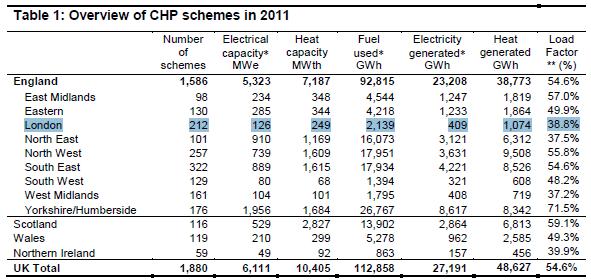 Table 1 highlights that there are 212 CHP schemes in London currently registered with the Government’s CHP Quality Assurance programme (more details at www.chpqa.com). This means that these generation plant have provided details of their operation to the QA programme and qualify for the benefits of being classed as ‘good quality’ such as exemption from the Climate Change Levy. A full list of where these 212 schemes are not unfortunately in the public domain, however, DECC do keep a subset of these schemes (32 listed at the time of writing) on their CHP database (run the region report for London). Additional schemes should also be able to be identified on the London Heat Map. Note – there are likely to be more than 212 schemes – small scale (say around 100kWe and below) CHP engines may not bother registering with the CHPQA as the financial benefits of the CCL exemption may only be modest for such plant.
Table 1 highlights that there are 212 CHP schemes in London currently registered with the Government’s CHP Quality Assurance programme (more details at www.chpqa.com). This means that these generation plant have provided details of their operation to the QA programme and qualify for the benefits of being classed as ‘good quality’ such as exemption from the Climate Change Levy. A full list of where these 212 schemes are not unfortunately in the public domain, however, DECC do keep a subset of these schemes (32 listed at the time of writing) on their CHP database (run the region report for London). Additional schemes should also be able to be identified on the London Heat Map. Note – there are likely to be more than 212 schemes – small scale (say around 100kWe and below) CHP engines may not bother registering with the CHPQA as the financial benefits of the CCL exemption may only be modest for such plant.
409 GWh of electricity were produced by these 212 CHP schemes in 2011. This represented 1.8% of the total CHP-electricity generated in England, and only 1.5% of electricity generated in the UK.
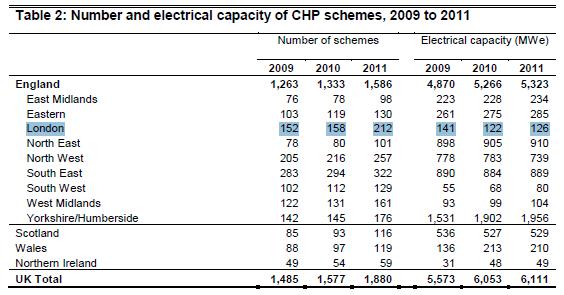 Table 2 however appears to show that, since 2009, there has been a net growth of 50 CHP schemes in London (ie some CHP plant may have been decommissioned – the actual number of new plant isn’t provided – only the net figure of 50). There has been a considerable revision of the numbers since last year’s dataset (for which, see story here) which reported that 188 Good Quality CHP schemes were operational in London as at the end of 2010, as compared with the 158 seen in the table above. Overall a confusing picture!
Table 2 however appears to show that, since 2009, there has been a net growth of 50 CHP schemes in London (ie some CHP plant may have been decommissioned – the actual number of new plant isn’t provided – only the net figure of 50). There has been a considerable revision of the numbers since last year’s dataset (for which, see story here) which reported that 188 Good Quality CHP schemes were operational in London as at the end of 2010, as compared with the 158 seen in the table above. Overall a confusing picture!
More importantly, there appears to have been a massive downward revision in the overall CHP capacity operating in London:
- Last year’s article indicated that there was 185 MWe (electrical capacity) of CHP operating in London in 2010. In contrast, the revised numbers today state only 122 MWe for the same year (2010).
- The latest data now reports that only 126MWe of CHP electrical generating capacity in London in 2011.
- Hence, whilst this latest data indicates a 4MWe increase in 2011 compared to 2010 all previous reports have indicated that approximately 200MWe of CHP capacity operated in London. Hence, this latest data suggests that there is in fact far less CHP operational in London than previously thought leading to a considerable downward revision!
- The 2011 statistics also report that this 126 MWe of CHP produced 409 GWh of electricity and 1,074 of heat GWh heat – a total of 1,483GWh energy in total – a drop by almost 50% of what we thought CHP was generating in London in terms of heat and power up to today as a result of previous DECC datasets.
- All in all, this does little to help the achievement of London’s 2025 25 per cent decentralised energy target – which is estimated in the Mayor’s Climate and Energy Strategy as a total of 23,500 GWh of energy [p86 – see chapter 4 of the Strategy for further information].
London Combined Heat and Power output falls
October 2011: DECC have just released their annual regional breakdown of Combined Heat and Power (CHP) statistics, providing further detail to the CHP chapter of DECC’s annual Digest of UK Energy Statistics, published in July of this year.
The statistics for London released indicate that:
- 188 Good Quality CHP schemes were operational in London as at the end of 2010
- These schemes amount to a total electrical capacity of 185 MWe and total thermal capacity of 372MWth
- They produced a total of 631GWh electricity and 1,680GWh heat – a total of 2,311 GWh energy
- Unlike many other regions, London does not have many large-scale industrial CHP schemes, which have typically long operational hours. Hence the overall load factor of London CHP schemes is low – the second lowest in the UK – at only 39.8%
- Importantly, whilst there has been a marginal increase in the number of CHP schemes operating in London (3 more in 2010) overall CHP generation capacity in London has decreased from 200MWe in 2009 to 185MWe. This is in despite an increase in overall increase in UK CHP capacity by over 500MWe.
- Additionally, when compared to last year’s statistics, the output from CHP plant in the capital has also fallen. CHP data as at the end of 2009 shows that CHP output stood at 746 GWh electricity and 2,414 GWh heat – a total of 3,160GWh of energy (see last year’s DECC Energy Trends September 2010 for details). Hence, as compared to the statistics just released, CHP energy output has dropped a significant 27% in the capital over one year. It’s difficult to determine exactly what is happening here without access to more detailed data for London from DECC – especially in relation to those schemes which may have retired.
- Note: there is a minor error in the latest Energy Trends article. Tables 5 & 6 suggest that 200MW CHP is operating in 2010. However, the report’s authors have clarified to energy for london that the correct capacity is 185 MWe and that:
- in Table 5 of the article, CCGT+GTs+STs should be 80 MWe and NOT 95 MWe. This will make the total for London 185 MWe, and consistent with Tables 1+2
- in Table 6 the London figure under the ’10 MWe and greater’ column should be 66 MWe and NOT 81MWe. This again will make the total for London 185 MWe, and consistent with Tables 1+2
Posted in Data Store, Decentralised Energy, News
Tagged CHP, Data, DECC, Decentralised Energy
Leave a comment
New Renewable Electricity Stats for London
30 September 2011: DECC have just released their annual regional breakdown of renewable electricity statistics, providing further detail to the renewable CHP chapter of DECC’s annual Digest of UK Energy Statistics, published in July of this year. (Note – this only refers to ‘renewable electricity’ and not ‘renewable energy’ which would include the contribution of renewables to heating and transport fuels also – the UK’s 2020 target is in relation to renewable energy).
The statistics for London indicate:
- 10 sites in London are indicated under the ‘wind and wave’ category to a total of 3.7 MWe. Virtually all of this capacity must be wind, and the vast proportion of it attributable to a single scheme – the Ford Dagenham wind turbine project.
- 6 schemes are classed under ‘other biomass’ a total of 110.6 MWe (note – these statistics only refer to ‘renewable electricity’ and not ‘renewable energy’, hence it does not include biomass heat-only schemes in London or elsewhere). The majority of this capacity must be from biogas to electricity schemes at Thames Water sewage waste water treatment plants, and also a Thames Water ‘sludge powered’ generator, and a number of landfill gas schemes.
- And then there are 1,044 solar PV schemes operating in London – to a total of 2.8MWe generation capacity (on PV installations in London see here for further detail).
- London has the lowest total overall renewable electricity output of all regions at 385GWh – exactly the same amount generated as in 2009 (see DECC Energy Trends September 2010 for details)
- The Mayor will shortly be issuing a detailed study on the potential for decentrailsed energy in London, including the use of renewable energy resources.
Posted in Data Store, News, Renewable Energy
Tagged Data, DECC, Mayor, Renewable Energy
Leave a comment